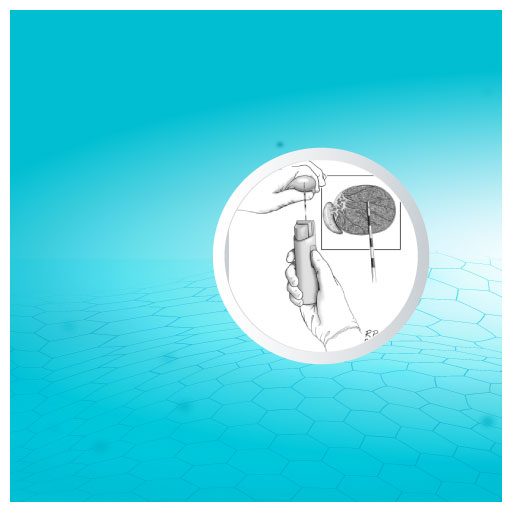
Testicular sperm aspiration (TESA) is a minimally invasive medical procedure specifically designed to retrieve sperm directly from the testicles. This technique is particularly beneficial for men who experience infertility due to conditions such as a prior vasectomy, congenital absence of the vas deferens, or obstruction that prevents sperm from being included in the semen during ejaculation. By employing a fine needle to extract sperm from the testicular tissue, TESA provides a viable option for couples looking to conceive through assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
The TESA procedure typically involves local anesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort. During the process, a urologist or reproductive specialist will insert a needle into the testicle to collect sperm cells, which can then be used for fertilization. One of the significant advantages of TESA is that it can be performed with a relatively quick recovery time and minimal complications. Importantly, the quality and motility of the sperm retrieved through TESA can often be sufficient for successful fertilization, making it an effective alternative for men with various reproductive challenges.